|
|
||||||||||||||
|
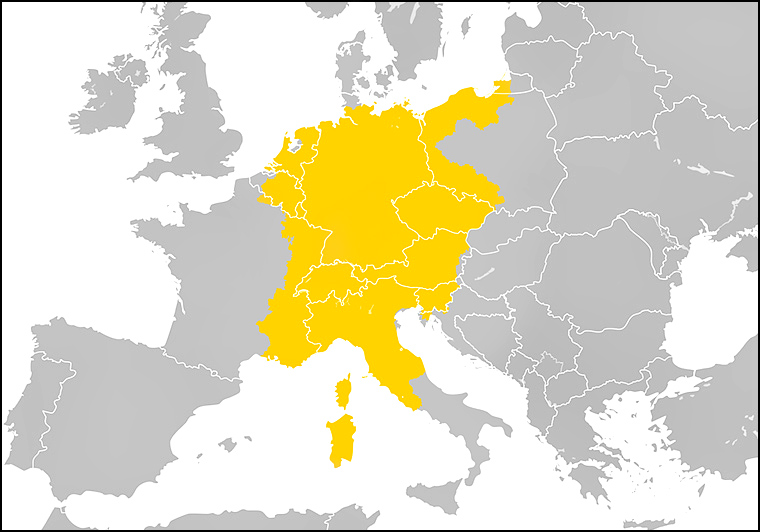
1 | Music In The Renaissance EraExploration, Rebirth and HumanismPeter Kun Frary
.
|
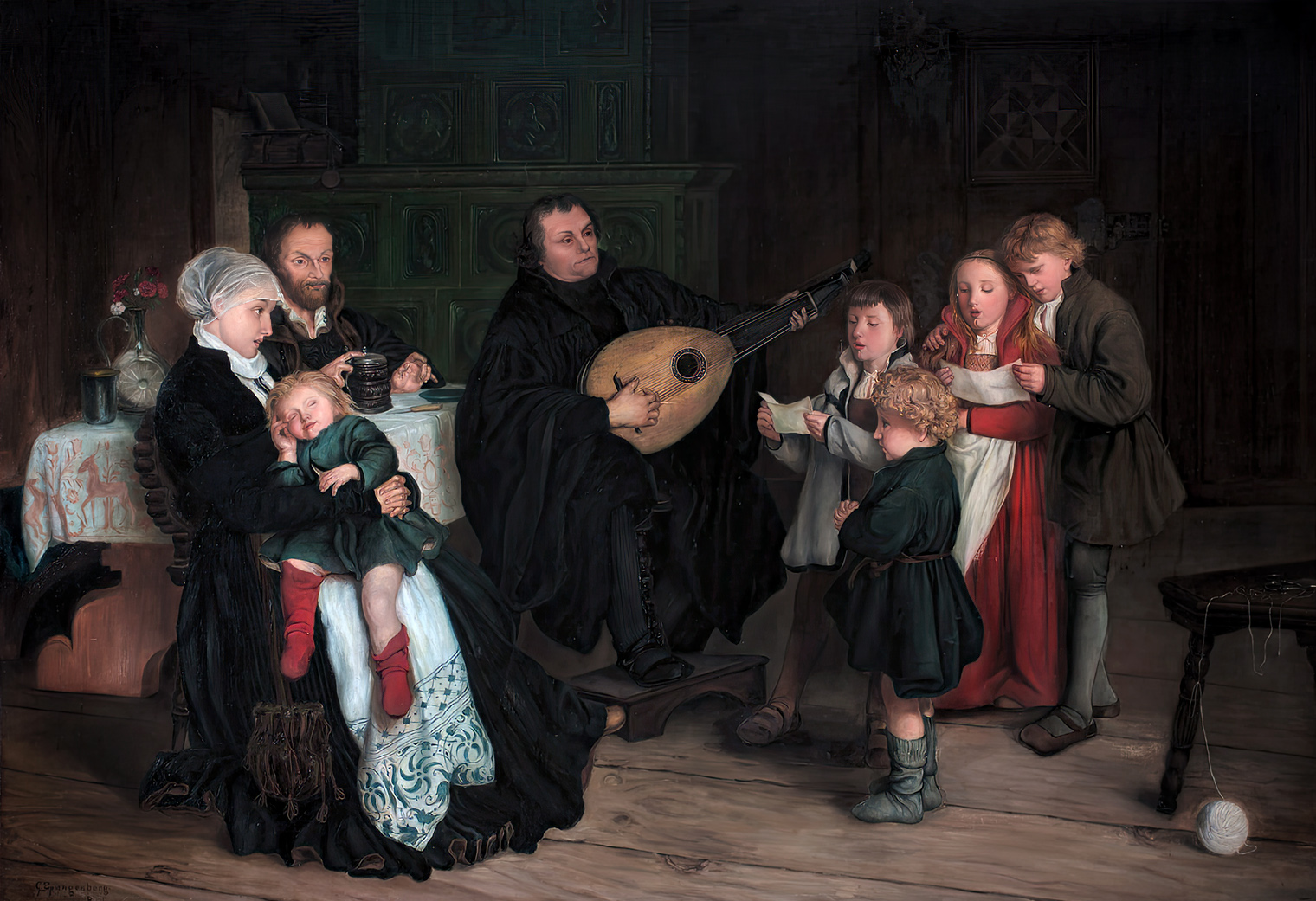
Changes in TheologyMartin Luther preached the doctrine of justification by faith, rather than by works, and railed against papal authority and the sale of indulgences. A prolific song writer, Luther penned the iconic hymn, A Mighty Fortress is My God (Ein feste Burg ist unser Gott), often referred to as the "Battle Hymn of the Reformation." Congregational Singing Luther introduced congregational singing in the vernacular—men and women singing together in church using their native language—and encouraged use of musical instruments in church. His reforms were revolutionary since, at the time, the Catholic Church only allowed a cappella singing in Latin by male cleric musicians. Although Latin was used in Lutheran services, German was increasingly preferred for singing, preaching and Bible studies. The role Luther granted to instrumental music and mixed choral singing in church greatly enhanced the development of music in Germany and Northern Europe. |
A Mighty Fortress is Our God | John Cavicchio, arr., plays an organ Chorale Prelude based on Luther's hymn (5:26).
Voyages of Discovery
The faltering of the Roman Catholic Church and Holy Roman Empire, two seemingly infallible institutions, set the stage for a flowering of European art and culture. Voyages of discovery by Christopher Columbus (1492), Ferdinand Magellan (1519) and others resulted in riches and opportunities pouring into Europe's port cities. The multitude of merchants and traders needed to man the new economy created a large and powerful middle class, a social class between nobility and peasantry. This class was also known as the merchant class and bourgeoisie, and was destine to be a consumer of art, music and literature.
The Renaissance was the beginning of the age of globalization. During this era, European powers and, subsequently, their former colonies, began political, economic, and cultural colonization of the world.
Book Publication
Education was no longer a monopoly of the Church. The printing press and an emerging middle class with leisure time created a demand for education. Nobility and the middle class found pride and status in education. Musical abilities were seen as a demonstration of high education and class status.
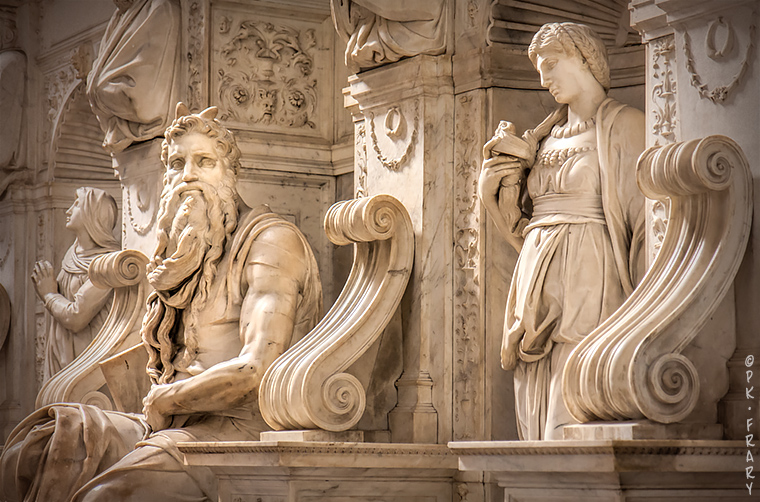
Moses | Michelangelo, 1475-1564 | Moses depicted with horns due to a poor Bible translation. | Basílica de San Pietro in Vincoli, Roma | ©Peter Kun Frary

 Patronage of Art and Music
Patronage of Art and Music
The Roman Catholic Church was still an important patron of the arts, but the Protestant Reformation reduced Church resources and influence. Thus, the most significant musical activities gradually shifted to royal courts. A typical royal court employed ten to sixty musicians for entertainment and chapel duties. Professional musicians were considered servants by noble patrons, but enjoyed a higher status in Renaissance society than they did during the Middle Ages. Now musicians were recognized as creative individuals and usually signed their works.
Vocabulary
Renaissance, Humanism, Protestant Reformation, Martin Luther, merchant class, middle class, bourgeoisie, Johannes Gutenburg
 |
 |
©Copyright 2018-25 by Peter Kun Frary | All Rights Reserved